Hana Multilingual Settings
Hana empowers teams to work in their preferred language. This guide explains how language preferences work, how to manage them, and what to expect across the platform.
1. Overview
- Organization-wide preference: Every organization has a single preferred language. It governs Hana’s system messages, notifications, and default response language.
- User-generated content: Users can converse or store information in any supported language. Hana automatically handles input in multiple languages.
- Automatic fallback: If Hana cannot determine a matching language, English is used as a fallback.
- Coverage scope: Localization applies to chat responses, memory notifications, polls, upgrade prompts, and most interface messages. Third-party connectors may offer partial localization.
2. Supported Languages
Hana currently supports the following languages:
- AR: Arabic
- DA: Danish
- DE: German
- EN: English
- ES: Spanish
- FA: Persian
- FI: Finnish
- FR: French
- GU: Gujarati
- HE: Hebrew
- HI: Hindi
- ID: Indonesian
- IT: Italian
- JA: Japanese
- KO: Korean
- MR: Marathi
- NL: Dutch
- PL: Polish
- PT: Portuguese
- RU: Russian
- SV: Swedish
- TA: Tamil
- TE: Telugu
- TR: Turkish
- UR: Urdu
- VI: Vietnamese
- ZH: Chinese
Additional languages may be introduced over time. If a required language is missing, contact Hana support to request it.
3. Choosing a Preferred Language
Through the Dashboard
- Sign in with an Admin account.
- Open Organization Settings → General.
- Select the desired Preferred Language from the list.
- Save changes.
Via API
- Organizations can programmatically set or update the preferred language using the Organization API. Include the ISO-style language code from the supported list.
- A companion endpoint returns the full list of languages, useful for building language pickers in custom interfaces.
4. How Language Preferences Affect Hana
- Chat Responses: Hana uses the organization’s preferred language for system prompts and standard replies.
- Memory Notifications: “Memory saved” confirmations and edit links are localized.
- Polls & Interactive Cards: Poll prompts, buttons, and follow-up messages appear in the preferred language.
- Upgrade & Plan Notices: Subscription reminders and upgrade cards respect language settings.
- Error & Status Messages: Common system messages (“Thinking…”, “Preparing…”) are localized.
- Third-Party Connectors: Connectors attempt to honor the setting, though some may still output English text.
5. Working With Multiple Languages
- Cross-language chat: Users may send messages in any supported language. Hana detects the input and replies in that language or in the organization’s default if detection fails.
- Mixed-language organizations: Members can converse in different languages simultaneously. Each request is evaluated independently.
- Memory ingestion: Content is stored exactly as provided. Hana does not translate memory text automatically, but it can retrieve and reference memories across languages.
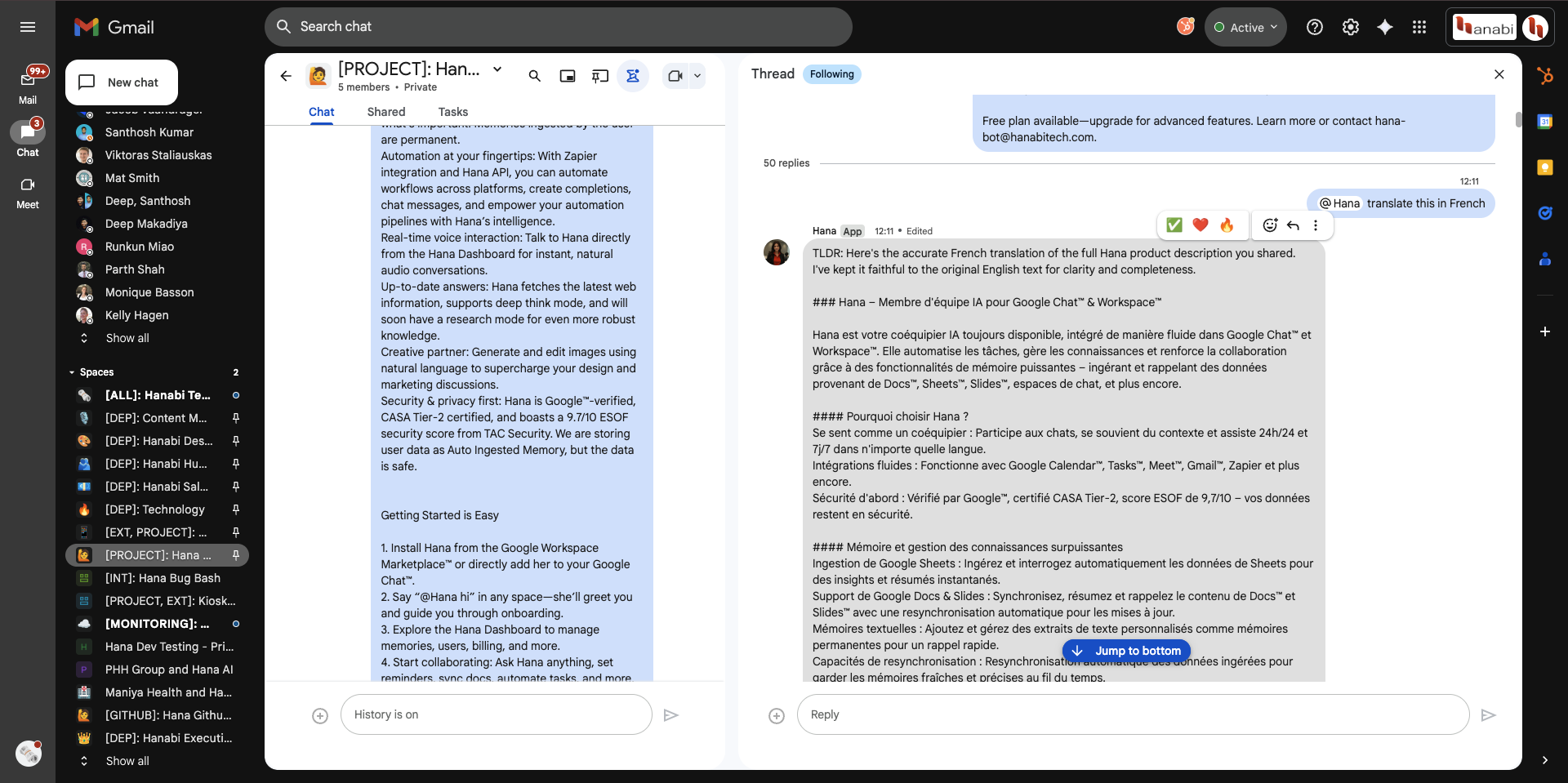 Example: Requesting a French translation of a long product description. Hana preserves fidelity to the source while formatting the response clearly.
Example: Requesting a French translation of a long product description. Hana preserves fidelity to the source while formatting the response clearly.
6. Fallbacks & Limitations
-
Unsupported Languages
If a user sends a message in a language not listed above, or if Hana cannot confidently identify it, English is used. -
Partial Localization
- Some specialized components or third-party integrations may show English labels.
- Custom workflow descriptions entered by admins are not automatically translated.
-
Translation Nuance
Machine-translated phrases may not reflect subtle regional variations. Encourage users to verify critical information. -
Model Restrictions
New languages are subject to model availability and quality. For niche languages, response quality may vary.
7. Best Practices
- Set language early: Configure the preferred language during onboarding so all members receive consistent messages.
- Educate users: Let team members know the chosen language and how to change it (if relevant).
- Monitor accuracy: For important communications (e.g., policy notices), review translations for clarity.
- Collect feedback: If users notice missing translations or incorrect phrasing, share it with Hana support for improvement.
- Plan for updates: When switching the preferred language, inform members that historical messages and existing memories remain in their original language.
8. Troubleshooting
- Hana responds in English despite chosen language: Verify that the organization’s preferred language is correctly set.
- Mixed-language responses within a single conversation: Ensure the user’s input language is supported; otherwise English is used.
- API update fails: Confirm the language code is valid and that Admin credentials are used.
- Third-party card still in English: Check if the external service provides localized text.
9. Summary
Hana’s multilingual capabilities enable organizations to collaborate in their native language without losing functionality. By setting a preferred language, teams receive localized system messages, memory prompts, and interactive content. Users remain free to converse in any supported language, and Hana adapts on the fly. Keep the supported language list handy, monitor for translation accuracy, and enjoy a seamless multilingual experience.
What it does
This tool area controls Hana language behavior for organization defaults and multilingual chat responses.
When to use
Use when your team needs consistent response language, cross-language collaboration, or explicit language overrides in chat.
Supported operations/arguments
| Operation | Invocation pattern | Arguments |
|---|---|---|
| Set org language | @Hana set organization language to <language> | language (supported language name/code) |
| Thread language override | @Hana respond in <language> for this thread | language |
| Translation request | @Hana translate this to <language> | source content + target language |
Invocation examples
@Hana set organization language to English.
@Hana respond in Spanish for this thread.
@Hana translate the previous update to French and keep bullet points.
More copy-paste examples
Language preference (organization-level):
@Hana set organization language to German.
@Hana set organization language to Japanese.
@Hana set organization language to Portuguese and confirm the change.
Per-thread language behavior:
@Hana for this thread, respond in Hindi.
@Hana keep this conversation in French unless I say otherwise.
@Hana in this thread, respond in Spanish and translate technical terms only when needed.
Troubleshooting
- Replies still in English: verify org preferred language and use an explicit per-message language request.
- Mixed-language output: simplify prompt and specify one target language.
- Unsupported language: Hana falls back to English.
Permissions/limits
- Organization-level language changes require admin privileges.
- Language quality may vary by model capability and language coverage.
High-signal invocation
@Hana set organization language to English and confirm the active language setting.
Edge-case invocation
@Hana in this thread, respond in Japanese and translate the previous message to English in bullet points.